Key Takeaways
- Use WiFi Analyzer to optimize signal range and frequency.
- Ensure proper signal strength (-50 to -55 dBm) throughout your space.
- Choose the right channels based on network frequency for optimal performance.
Buying a new Wi-Fi router isn’t enough to boost your network on its own. To make the most of your Wi-Fi, you need to ensure that you’re getting the best range, signal, and frequency. Thankfully, a handy mobile app will get you up and running in no time.
Why I Use WiFi Analyzer
There are plenty of apps for scanning Wi-Fi networks on the go, but only a few present data easy enough for novices to read. Wi-Fi Analyzer is a free, open-source Android app that can determine anything from the signal strength from a specific access point to the best channels to connect to and even estimate how far the access point is from you.
Download: WiFi Analyzer for Android (Free)
The app is divided into four sections:
- A list of access points, along with signal strength
- A list of all available channels with a rating assigned to each
- A channel graph
- A time graph.
All the data is very well laid out and easy to understand once you spend a few minutes reading the documentation provided on its GitHub Repository page or WiFi Analyzer website.
It was one of the first apps I downloaded when I first started tinkering with my Wi-Fi, and it has stuck with me since simply because of the easy-to-use interface, the no-nonsense functionality, and the fact that, despite being free, there are no in-app ads.
Ensure Good Wi-Fi Signal and Broadcast Range
The first step to boosting your Wi-Fi connection is to ensure a strong signal. If you’ve just set up your router, one of the first things you should do is fire up the WiFi Analyzer and walk around your home or office to ensure proper signals in each room.
Wi-Fi signals are measured in decibel milliwatts (dBm) and range from -30 dBm to -90 dBm. The higher the number, the worse your signal gets. Ideally, you’d want no more than -50 to -55 dBm.
If your signal strength is low, consider using an old router you might have lying around as a repeater. You can also invest in a mesh Wi-Fi network to ensure different parts of your home or office are well within the Wi-Fi range.
Use the Right Wi-Fi Channels
Wi-Fi channels are an important factor in ensuring that you get the most out of your Wi-Fi network.
The Wi-Fi channel you use depends on the Wi-Fi band you’re using. Whether on a 2.4GHz, 5GHz, or 6GHz network, the goal is to be on the least congested Wi-Fi channel. A quick glance at the Channel Rating page in WiFi Analyzer will show you ratings of each channel available from your access point.
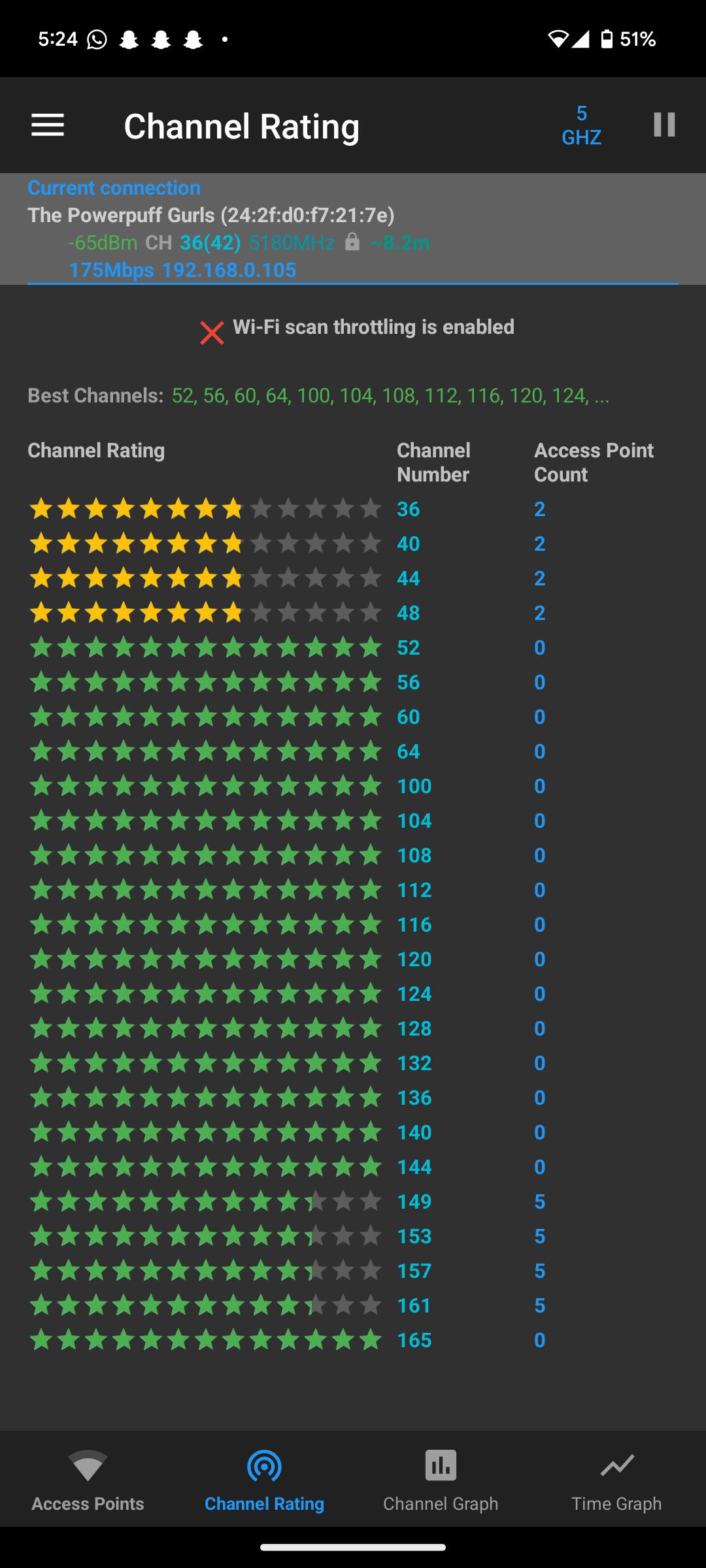
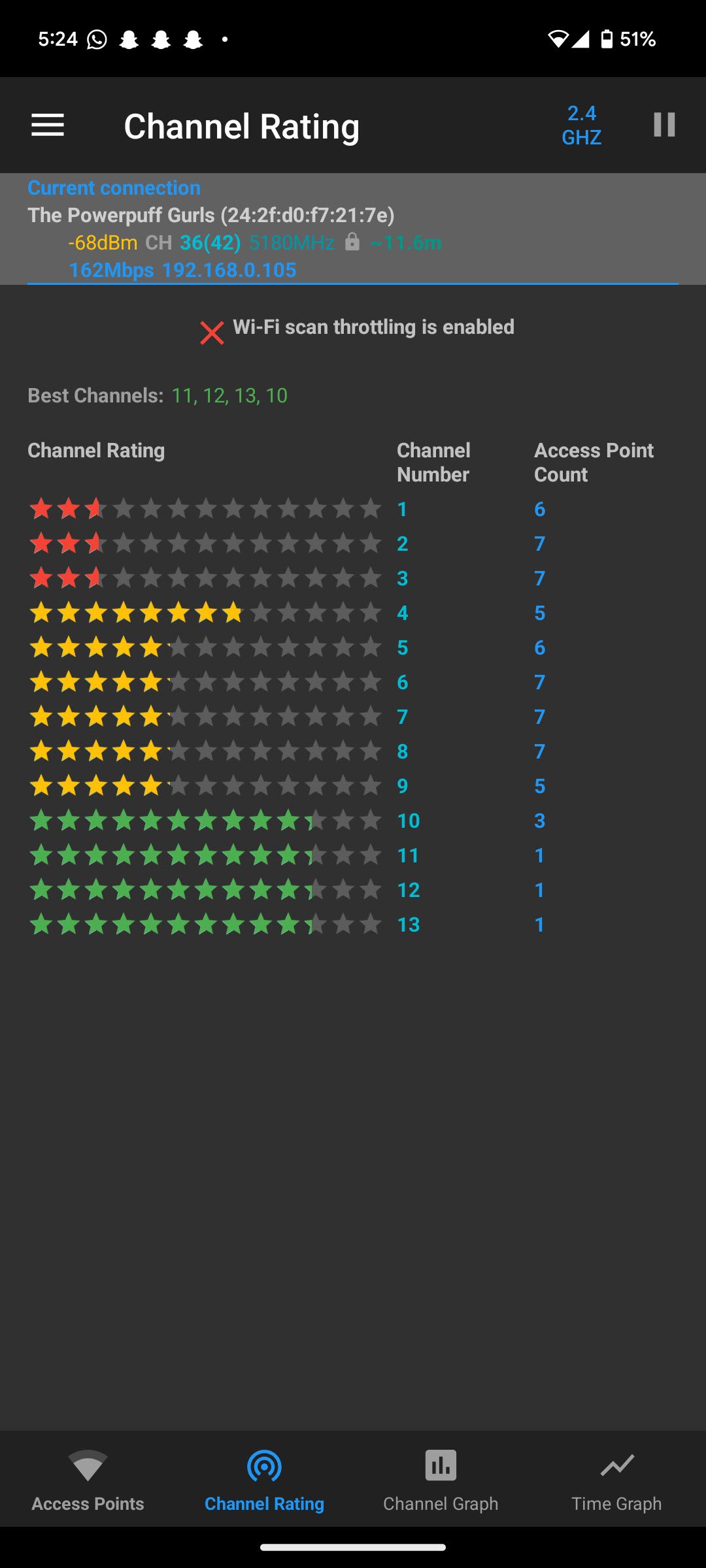
Generally speaking, channels 1, 6, and 11 are best if you’re on a 2.4GHz network. However, this will vary depending on where you are and how much interference your router is dealing with, so it’s important to check out the correct Wi-Fi channels when setting up your network.
When using a 5Ghz or 6GHz network, the number of available channels increases, meaning you get more channels that aren’t getting as much interference and, hence, better speeds. Your Wi-Fi router will automatically try to provide the best channels to connect to, but it can get them wrong often, meaning it’s best if you manually pick the channels you want to use.
The channel width also matters. If you’re on a 2.4GHz network, set the channel width to 20MHz for better reliability, as 40MHz tends to catch a lot of interference. On 5GHz or better networks, you can push the channel width to 40MHz without much interference. 80MHz and 160MHz channel widths might give you better speeds but will also catch more interference, affecting your network’s reliability.
Wi-Fi Band Matters
Last but not least, the Wi-Fi frequency (band) you’re using matters a lot. From a range standpoint, 2.4GHz is the best. However, it also receives the most interference from anything, including, but not limited to, other routers in your vicinity, any Wi-Fi repeaters you might’ve set up, microwaves, and even baby monitors.
5GHz and 6GHz bands work better because they use channels unused by other devices and anything else that uses wireless communication. They’re still susceptible to interference, just far less than the 2.4GHz band. So, if your router doesn’t support them, you should consider buying a new router with these essential features.
Your choice of band will also depend on the range you want. The wider channel widths offered by 5GHz and 6GHz bands don’t work well over longer ranges. So, if you’ve got the main router set up far away from your desk, you’re going to either have to run a repeater, a mesh network, or a good old-fashioned ethernet cable—which is still the best way to get the fastest, most stable connection to the internet.
Overall, with a little tweaking and research, you can optimize your Wi-Fi network for your particular surroundings to get the most out of your internet bandwidth and boost your Wi-Fi network—at no extra cost.




