- Gold price drifts higher in Monday’s Asian session.
- Safe-haven demand amid US presidential election uncertainties, persistent Middle Eastern tensions, might lift the Gold price.
- Traders brace for the US election outcome on Tuesday ahead of the Fed rate decision.
The Gold price (XAU/USD) trades in positive territory on Monday. The US presidential election risks and the ongoing Middle East geopolitical tensions are likely to underpin the yellow metal, a traditional safe-haven asset, in the near term. Nonetheless, the renewed Greenback demand and higher US bond yields might cap the upside for Gold price as higher yields make non-yielding assets like bullion less attractive in comparison.
Investors will closely watch the looming US presidential election on Tuesday. The attention will shift to the US Federal Reserve (Fed) rate decision on Thursday. The uncertainty over the US election outcome is one reason markets assume the Fed will deliver a rate cut of the usual 25 basis points (bps) on Thursday, rather than repeat its outsized half-point easing.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price remains strong ahead of US presidential election
- “ETFs should see further inflows due to the expected interest rate cuts, high fiscal deficits and the highly valued stock markets. However, investment demand in the fourth quarter could be heavily influenced by the outcome of the US elections. The central bank’s Gold purchases are likely to be strong again this year, but not at the levels seen in the previous two years. Jewelry demand is also expected to be lower than in the previous year, albeit somewhat higher than previously expected by the WGC,” noted Commerzbank analysts.
- PredictIt has placed a 51% chance of a Harris win on Tuesday, marking the vice president’s first lead over Trump (who leads Harris at a 49% chance) on the site since October 9.
- The US NFP increased by 12K in October, the smallest gain since December 2020. This figure followed the 223K rise (revised from 254K seen in September) and below the market consensus of 113K, by a wide margin.
- The Unemployment Rate was unchanged at 4.1% in October, matching the expectations.
- Financial markets have fully priced in a 25 basis points (bps) rate cut by the US Federal Reserve (Fed) at its November meeting on Thursday.
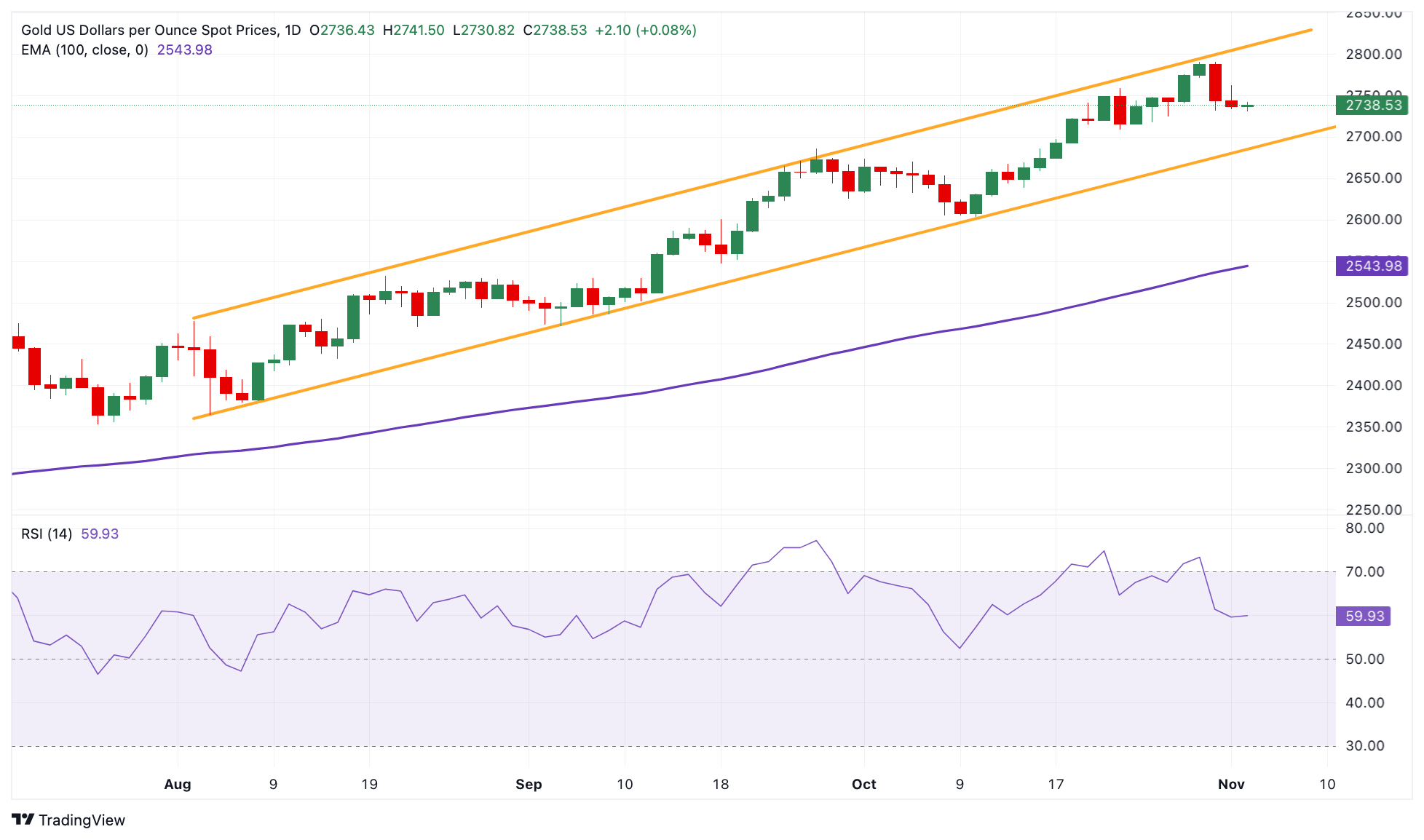
Technical Analysis: Gold price keeps the bullish vibe in the longer term
The Gold price edges higher on the day. The positive picture of the precious metal prevails as the price holds above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on the daily chart. Furthermore, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) stands above the 50-midline near 60.20, suggesting the support level is likely to hold rather than break.
More green candlesticks above the all-time high and psychological mark in the $2,790-$2,800 zone could bump XAU/USD to $2,850.
On the other hand, consistent trades below $2,715, the low of October 24 might drag the yellow metal to $2,624, the low of September 30, followed by the $2,600 round mark.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.